Sariah Mghames, Luca Castri, Marc Hanheide and Nicola Bellotto
Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Cybernetics and Intelligent Systems (CIS) and IEEE International Conference on Robotics, Automation and Mechatronics (RAM)
Abstract
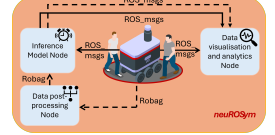
Autonomous mobile robots can rely on several human motion detection and prediction systems for safe and efficient navigation in human environments, but the underline model architectures can have different impacts on the trustworthiness of the robot in the real world. Among existing solutions for context-aware human motion prediction, some approaches have shown the benefit of integrating symbolic knowledge with state-of-the-art neural networks. In particular, a recent neuro-symbolic architecture (NeuroSyM) has successfully embedded context with a Qualitative Trajectory Calculus (QTC) for spatial interactions representation. This work achieved better performance than neural-only baseline architectures on offline datasets. In this paper, we extend the original architecture to provide neuROSym, a ROS package for robot deployment in real-world scenarios, which can run, visualise, and evaluate previous neural-only and neuro-symbolic models for motion prediction online. We evaluated these models, NeuroSyM and a baseline SGAN, on a TIAGo robot in two scenarios with different human motion patterns. We assessed accuracy and runtime performance of the prediction models, showing a general improvement in case our neuro-symbolic architecture is used. We make the neuROSym package 1 publicly available to the robotics community.
@INPROCEEDINGS{10672815,
author={Mghames, Sariah and Castri, Luca and Hanheide, Marc and Bellotto, Nicola},
booktitle={2024 IEEE International Conference on Cybernetics and Intelligent Systems (CIS) and
IEEE International Conference on Robotics, Automation and Mechatronics (RAM)},
title={neuROSym: Deployment and Evaluation of a ROS-based Neuro-Symbolic Model for Human Motion Prediction},
year={2024},
volume={},
number={},
pages={57-62},
keywords={Visualization;Runtime;Accuracy;Tracking;Navigation;Neural networks;Random access memory},
doi={10.1109/CIS-RAM61939.2024.10672815}}

